COSHH
(CONTROL OF SUBSTANCES HAZARDOUS TO HEALTH REGULATIONS,
2002)
INTRODUCTION
The Control of Substances
Hazardous to Health Regulations first came into force in the 1st of October
1989 in U.K. and it applies to all types of businesses. COSHH requires employers to control substances that are hazardous to health
and protect workers from harmful substances
COSHH applies to a wide range of substances and preparations (mixtures of two or more substances) which have the potential to cause harm to health if they come in contact either through ingestion, inhalation, absorption.
Hazardous substances do not mean HIGH-RISK CHEMICALS TOXIC CHEMICALS which are easily recognizable, but also common substances like paints, inks, cleaning agents, soaps, dyes, bleaching agents, sprays, etc.
So, a hazardous substance can be any substance in any form that can cause harm to health like
1. Chemicals
2. Dust
3. Fumes
4. Vapors
5. Gases
6. Biological agents
Substances that do not come under COSHH, but are covered under separate regulations as they are more hazardous and require more controls while handling
1. Lead
2. Asbestos
3. Radioactive substances
4. Biological agents not connected with work etc
COSHH RESPONSIBILITIES
In order for proper implementation of COSHH, there are certain responsibilities for both EMPLOYERS and EMPLOYEES which should be followed for effective implementation of COSHH requirements.
COSHH RESPONSIBILITES
FOR EMPLOYERS: The Main responsibility of EMPLOYERS
is to protect people from any harm that hazardous substances may cause in the workplace.
In order for the effective implementation of COSHH, the following 8 steps are to be
followed.
1.
COSHH Risk Assessment:
This requires identification of all the hazardous substances within the activity defined, those substances include which are being used and which are being produced, The following information is looked for understanding whether a substance is hazardous or not, a COSHH INSPECTION needs to be carried out, it is understanding the workplace and finding out processes that can produce fumes, vapors, mist or gas and liquids that potentially affect the health of the people, other areas to look for are:-
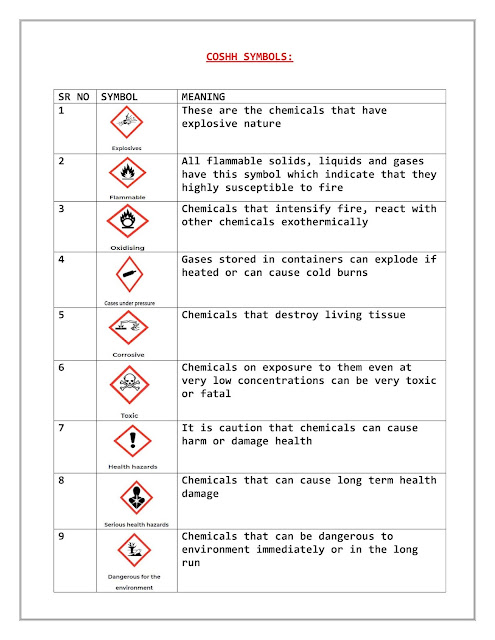
1. Labels and Hazard symbols
2. Supplier data
3. Manufacturer data
4. Employee Data
5. Health Surveillance Data
The following
points to follow for evaluating risk assessment
· All hazardous substances to the identified and listed in the workplace
· The implications on health for each hazardous substance need to be
evaluated.
· Assessing who may be affected and how it involves all the persons
likely to get exposed
· The exposure routes can include inhalation, ingestion, or absorption
· All the observations and findings to be recorded.
2. Precautions need to be taken:
· Use of possible alternatives
· Check for process change
· Reviewing existing control
measures and their effectiveness
3. Ensure Prevention and control measures are adequate
· Checking for controlling the exposure at source
· Change in equipment that removes the hazard
· Storing conditions of hazardous
substance
· PPE designed based on the properties
of hazardous substances
4. Maintain control measures:
· Train and educate employees on how to use the control measures properly
· Provide conditions where deviations
or problems in controls measures are encountered, they can be easily reported
· Checking regularly for implemented
procedures
5. Monitoring Exposure
· Measuring the concentration of the hazardous substance in the air to check the WEL (workplace exposure limits) whether they are in range (or) surpassed the exposure limits which can cause serious health
6. Use suitable health surveillance: The health surveillance
includes
·Checking for skin conditions
· Lung function tests, breathing assessment tests
· To identify any disease that can occur when using a particular
substance
7. Give information instruction and training: All employees are to be trained and provided with guidelines and
relevant instructions, their training and guidance should be in the areas
· Access to and understanding of safety data sheets
· All hazardous substances names, condition, and their effect on health.
· The findings of RISK ASSESSMENT
· The Understanding of control measures and precautions they employees
should take to protect themselves and others
· Reporting of observations, faults or deviations if any encountered
while taking up control measures.
·Usage of PPE
· Understanding emergency procedures
·All the results of EXPOSURE MONITORING and HEALTH SURVEILLANCE
8. Put in place procedures for accidents, incidents and emergencies:
During any unforeseen accident, there should be necessary
process and procedures to handle such a situation. This requires proper
planning
·Setting up emergency systems and warning systems
· The information regarding emergency services is in place so that
everyone is aware and knows how to use it.
· All staff and workers to participate in regular safety and mock
drills
· A clear procedure and plan should be in place which outlines the
steps that reduce the harmful effects and restore situation to normal
· A proper communication system for all the employees who are affected
· Ensuring that there is necessary safety equipment in place to deal with any emergencies.
COSHH RESPONSIBILITES
FOR EMPLOYEES: The Main responsibility of EMPLOYEES
is to take reasonable care and protect themselves by effectively using all the
control measures provided. The main things employee should follow are
1. Effective use of control measures
2. Reporting of any defects found
3. Attend health surveillance as required
4. Incident and Accident reporting
WORKPLACE EXPOSURE LIMITS (WEL): WEL is concentrations of hazardous substances in air. Hazardous substances under COSHH are assigned Workplace exposure limits (WELs) which must not be exceeded.
It is calculated for
· LTEL (LONG TERM EXPOSURE LIMIT) - 8-hour period
· STEL (SHORT TERM EXPOSURE LIMIT) – 15 Minute period
Article by PJ Mohan
Sr.Faculty, NIFS




No comments:
Post a Comment